Immunotherapy
What is immunotherapy?
Immunotherapy is a type of treatment developed to boost the body’s immune system to help oppose certain types of diseases. Also defined as biologic therapy,
it is mainly designed for cancer treatment using organic or synthetic substances to prevent the spread of cancer cells. It also enhances the function of the immune system, specifically in targeting carcinogenic cells and quashing certain immune reactions.
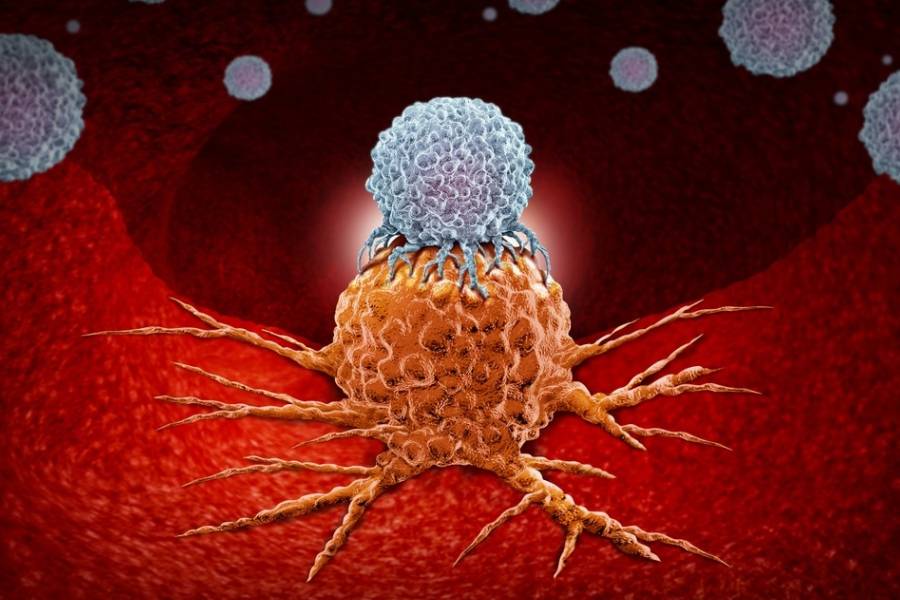
The body’s first line of defense is the immune system, where component cells and substances work together to kill different pathogens and foreign bodies that generate infections and diseases. Cancer cells, however, are not foreign bodies but are earlier healthy cells that unexpectedly alter and grow, making it hard for the immune system to notice, track, and attack them.
Aside from cancer, immunotherapy is also used to treat severe allergic disorders and autoimmune diseases as well as control organ rejection for organ transplant patients.
There are many types of immunotherapy including monoclonal antibodies, T-cell therapy, cancer vaccines, oncolytic virus therapy, and non-specific immunotherapy, among others. New approaches are consistently being developed to continually address a wide range of cancer types and other medical needs.
Who Should Undergo and Expected Results?
Dr. Pratik Patil recommended Immunotherapy for:
- Cancer patients – Immunotherapy is especially helpful for patients with different types of cancer. To gain maximum results, this therapy is often given with conventional treatment methods such as chemotherapy.
- Patients with a persistent bacterial infection – Immunotherapy is also suitable for treating continuous bacterial infections like hepatitis C and HHV6 infections.
- Organ transplant recipients – These patients also experience immunotherapy to stop the immune system reaction against the newly transplanted organ so the body will not abandon it.
- Patients with autoimmune diseases – Immunosuppressive drugs are also used to manage autoimmune diseases.
- Allergy patients – Patients suffering from various allergies are also recommended to try immunotherapy to reduce the body’s responses to specific allergens. In this case, immunotherapy is used not to treat an allergy but to minimize its severity. This type of treatment is typically indicated for those prone to intense allergic attacks and who cannot avoid exposure to allergens.
- As for the desired results, most patients report improved conditions following immunotherapy sessions. However, the success of the treatment depends on several factors. Such as the intensity of cancer or disease at the onset of treatment, the physical condition of the patient, therapy’s duration, and responsiveness of the body’s immune system is. There have been substantial breakthroughs in various areas of cancer treatment research, specifically when immunotherapy is given with other treatment modalities.
How is the Procedure Performed?
Most immunotherapy agents have distributed through the IV (Intravenous ) method or injected the substance directly into the vein for faster absorption. An example of this type of therapy is the introduction of cytokines through IV to fight off tumor cells. Therapies involving immune system blockade are also typically distributed through IV.
There are also topical immunotherapy agents available. Different skin cancers and diseases are being treated with the use of an immune enhancement cream directly to the skin. Immunosuppressive medications are also taken orally. This method involves most transplant patients, who are given oral immunotherapy agents for immune suppression.
Another choice for distributing immunotherapy is going directly into the bladder. Termed intravesical therapy, is specially designed for the therapy of early stages of bladder cancer. This process involves the insertion of a catheter into the urethra and directing it to the bladder. Attenuated bacteria taking immunotherapy agents are then injected via the catheter.
Possible Risks and Complications:
Those getting immunotherapy intravenously may undergo pain and swell at the needle site.
Some patients report outbreaks of nausea and vomiting following immunotherapy sessions. In some cases, fever and chills occur as the immune system reacts to the substances being submitted to the body. Other signs reported are fatigue, unstable blood pressure, headache, and muscles pain. Others experience hair loss and improved risk of infections.
There is also the possibility of heart pulsations, diarrhea, and weight gain due to fluid retention. Edema or swelling due to fluid buildup is also one intricacy reported in some cases. Extreme allergic reactions can also happen, though this rarely occurs. Some immunotherapy agents can also induce harmful reactions in the body if distributed for a long period of time.
Looking for immunotherapy in Pune?
Dr. Pratik Patil is the best oncologist in Pune with experience of more than 12 years. He has special interests in immunotherapy treatment. For more information about cancer and treatment options, or to book an appointment with the Cancer Specialist in Pune call +919637439163 or Click on Book Appointment for online booking.
WhatsApp us
